Prototype
- 7 mins-
Prototype nedir?
“prototip”, “asıl örnek” anlamına geliyor.
- Amaç:
- Yeniden oluşturulması zaman alan nesneyi klonlamak/kopyalamak.
- Sınıf karmaşıklığını ve kullanılan sınıf sayısını azaltmak.
- Çözüm:
- Klonlanacak prototip nesneyi oluşturmak.
- implements Cloneable
- +clone()
- Setter
- Klonlanacak prototip nesneyi oluşturmak.
-
Ek bilgiler: Prototype yerine Abstract Factory ya da Factory Method kalıpları kullanabilirdi. Aralarındaki fark Factory kalıtım kullanırken(bu her yeni nesne için bir factory nesnesi gerekmesi anlamına gelir), Prototype ise var olan prototip nesnesinden türetilir.
- İlişkili Tasarım Kalıpları;
- Abstract factory
- Factory Method
- Decorator
- Composite
-
Final Code
Örneğimize ait UML diagramı
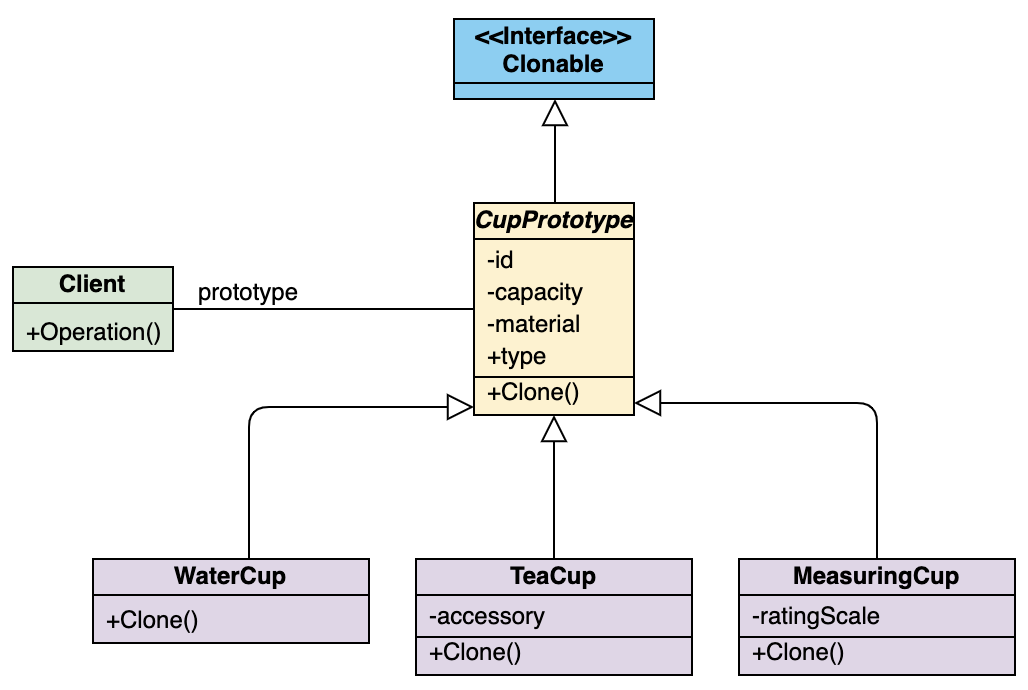
“CupPrototype” klonlayacağımız prototip nesnesini temsil ediyor.
public abstract class CupPrototype implements Cloneable{
private int id;
protected double capacity;
protected String material;
protected String type;
public CupPrototype(int id, double capacity, String material) {
this.id = id;
this.capacity = capacity;
this.material = material;
}
public int getId() {
return id;
}
public void setId(int id) {
this.id = id;
}
public double getCapacity() {
return capacity;
}
public void setCapacity(double capacity) {
this.capacity = capacity;
}
public String getMaterial() {
return material;
}
public void setMaterial(String material) {
this.material = material;
}
public String getType() {
return type;
}
public void setType(String type) {
this.type = type;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "CupPrototype{" +
"id='" + id + '\'' +
", capacity=" + capacity +
", material='" + material + '\'' +
", type='" + type + '\'' +
'}';
}
public Object clone() {
Object clone = null;
try {
clone = super.clone();
} catch (CloneNotSupportedException e) {
System.out.println("Problem when cloning the object: " + e.getMessage());
e.printStackTrace();
}
return clone;
}
}
Prototip nesnesini extends eden diğer 3 nesnemiz.
public class WaterCup extends CupPrototype{
public WaterCup(int id, double capacity, String material) {
super(id, capacity, material);
type="WaterCup";
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "WaterCup{" +
"capacity=" + capacity +
", material='" + material + '\'' +
", type='" + type + '\'' +
'}';
}
}
public class TeaCup extends CupPrototype {
private String accessory;
public TeaCup(int id, double capacity, String material,String accessory) {
super(id, capacity, material);
type="TeaCup";
this.accessory=accessory;
}
public String getAccessory() {
return accessory;
}
public void setAccessory(String accessory) {
this.accessory = accessory;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "TeaCup{" +
"accessory='" + accessory + '\'' +
", capacity=" + capacity +
", material='" + material + '\'' +
", type='" + type + '\'' +
'}';
}
}
public class MeasuringCup extends CupPrototype {
private String ratingScale;
public MeasuringCup(int id, double capacity, String material,String ratingScale) {
super(id, capacity, material);
type="MeasuringCup";
this.ratingScale=ratingScale;
}
public String getRatingScale() {
return ratingScale;
}
public void setRatingScale(String ratingScale) {
this.ratingScale = ratingScale;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "MeasuringCup{" +
"ratingScale='" + ratingScale + '\'' +
", capacity=" + capacity +
", material='" + material + '\'' +
", type='" + type + '\'' +
'}';
}
}
Son olarak test nesnemizi yazıyoruz.
public class Client {
public static void main(String[] args) {
TeaCup slenderTeaCup = new TeaCup(1, 100, "glass", "tea plate");
System.out.println(slenderTeaCup);
TeaCup cup = (TeaCup) slenderTeaCup.clone();
cup.setId(2);
cup.setAccessory("handle");
System.out.println(cup);
}
}
Kod çıktısı:
TeaCup{accessory='tea plate', capacity=100.0, material='glass', type='TeaCup'}
TeaCup{accessory='handle', capacity=100.0, material='glass', type='TeaCup'}
Bu makaledeki kodu GitHub sayfamda bulabilirsiniz.
